01135348006
TACHOGRAPHS
Tachograph Analysis
Allow us to remotely analyse your tachograph data - Contact us Today!
Provide weekly feedback & flag any concerns
Ensure Tachograph Compliance
Automate vital reports
Account for all missing mileage
Flag all Infringements & Completion
Tachographs
Understanding Tachographs & Tachograph Rules
A tachograph is a device used to record driving time, rest periods, and other relevant data for drivers of commercial vehicles. It helps regulate drivers' work hours and ensure compliance with regulations like the Work Time Directive. Tachographs can be either manual or digital, and both types require calibration to ensure accuracy. Tachograph calibration is generally performed every 2 years.
Tachographs use a series of symbols to indicate different events, such as driving, rest, and breaks.
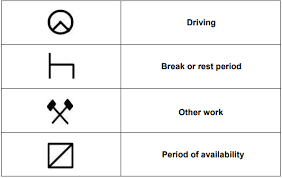
Drivers need to be familiar with these symbols to avoid any confusion and ensure that their records are accurate. They also need to understand tachograph rules to avoid any penalties or fines for non-compliance.
Tachograph exemption may be granted in certain circumstances, such as for vehicles used for emergency services or vehicles used for short distances. However, this exemption must be applied for and granted by the relevant authorities.
Tachograph analysis software, such as Tachomaster and Trutac, can be used to download and analyse tachograph data. These software programs can generate reports that provide valuable insights into a driver's activity and compliance with regulations.
Tachograph paper roles were used in manual tachographs, but digital tachographs use smart cards called tachograph cards. These cards hold the driver's information and data recorded by the tachograph. The data can be downloaded from the card using tachograph data download devices.
Tachograph problems can arise due to incorrect use or calibration, which can result in inaccurate records. Drivers and fleet managers must be vigilant to ensure that the tachograph is functioning correctly and that their records are accurate.
Switch mode is a feature in digital tachographs that allows drivers to switch between different activities, such as driving, rest, or other work. Drivers need to ensure that they switch mode correctly to ensure accurate records.
In conclusion, tachographs are an essential tool for regulating drivers' work hours and ensuring compliance with regulations. Drivers and fleet managers must be familiar with tachograph symbols, rules, and software to ensure accurate records and avoid penalties or fines. Calibration, data download, and proper use are crucial to avoiding tachograph problems and maintaining compliance.
Tachograph Rules & Regulations
In the UK, tachograph rules are governed by the European Union's drivers' hours regulations, which are designed to ensure that commercial drivers comply with certain safety standards and don't work excessive hours. The rules apply to drivers of goods vehicles with a maximum permissible weight of more than 3.5 tonnes and to drivers of passenger-carrying vehicles with more than nine seats. The rules are designed to ensure compliance with EU and UK driving time regulations, which aim to prevent driver fatigue and promote road safety.
Here are some key points of the tachograph rules in the UK:
Tachographs must be used to record driving time, breaks, and rest periods. These records must be kept for at least 28 days.
The maximum driving time for drivers is 9 hours per day, or 10 hours twice a week. A driver may not exceed 56 hours of driving time in any one week or 90 hours in any two consecutive weeks.
A driver must take a break of at least 45 minutes after driving for 4.5 hours. Alternatively, the driver may take a break of 15 minutes followed by a break of 30 minutes.
A driver must take a daily rest period of at least 11 hours, which may be reduced to 9 hours no more than 3 times per week.
A driver must take a weekly rest period of at least 45 consecutive hours. This may be taken in two periods, one of which must be at least 24 hours long.
Tachographs must be calibrated and tested at least every two years, and the records they produce must be accurate and tamper-proof.
Penalties for non-compliance can include fines, suspension or revocation of the driver's license, and even imprisonment in extreme cases.
It's worth noting that the tachograph rules are subject to change, and it's important for drivers and transport companies to stay up-to-date with any revisions or updates to the regulations. Failure to comply with tachograph rules can result in fines, disqualification from driving, or other penalties. It is important for drivers and operators to be aware of these rules and ensure that they are followed at all times
How to Apply for a Tachograph Card
To get a tachograph card in the UK, you need to follow these steps:
Determine the type of tachograph card you need: There are different types of tachograph cards available depending on your occupation, including driver, company, and workshop cards.
Complete the relevant application form: Once you know which type of card you need, you can download the application form from the gov.uk website or obtain a copy from a local Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA) office.
Provide necessary documentation: You will need to provide certain documents, such as proof of identity, proof of address, and proof of employment.
Pay the fee: The cost of a tachograph card varies depending on the type of card you need, and you can find the fees on the DVLA website.
Submit your application: You can submit your application form and supporting documents to the DVLA by post or in person at a local DVLA office.
Wait for your card to arrive: It can take up to 15 - 28 working days to receive your tachograph card by post, you can pay extra for a quicker delivery.
Do not drive without a Tachograph Driver card unless you have already ordered the new card, you will be given a unique number that confirms you have ordered the card, keep the evidence on your person whilst driving without a card. Print and store the daily tachograph prints outs. If possible take extra downloads of vehicle downloads during this period.
Note that there may be additional requirements or procedures depending on the specific type of tachograph card you need. It's always best to check with the DVLA or consult their website for more information. If you need any additional information or help with the application process, you can contact the DVLA on 0300 790 6801.