Understanding the Back Side of the British Driving Licence
Zed Aziz
The back of the British driving licence contains vital information that outlines the types of vehicles a driver is permitted to operate. This blog will comprehensively explain the significance of columns 9, 10, 11, and 12, focusing on the various driving licence categories and codes.
Columns Overview
Column 9: Vehicle categories you are entitled to drive.
Column 10: Start date
Column 11: End Date
Column 12: Additional driving licence codes and relevant details.
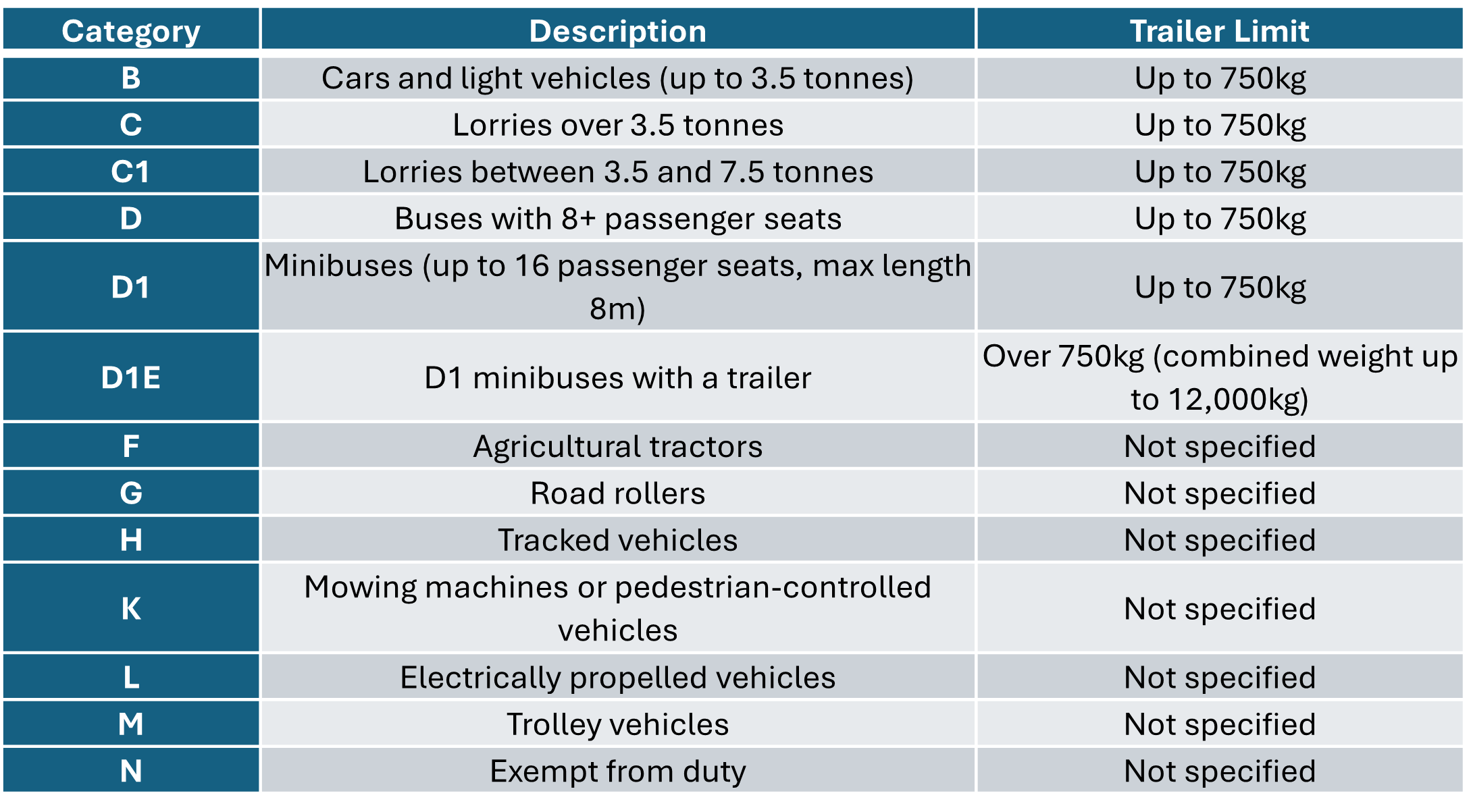
Driving Licence Categories
To help you easily identify what each category entails, we’ve created a grid below that categorises the various vehicle types and their corresponding driving licence requirements.
Driving Licence Codes in Column 12
Column 12 of the driving licence includes additional codes that provide further information about restrictions, endorsements, or special permissions related to a driver's entitlement. Here are some common codes.
What are Driving Licence Codes?
Driving licence codes stipulate the conditions you must meet before you can get behind the wheel. There are more than 50 driving licence codes, each specifying different requirements and limitations. Some of the common ones include:
Additionally, some codes address vehicle modifications to ensure safe operation according to individual needs.
01: Eyesight correction (e.g., glasses or contact lenses).
02: Hearing/communication aid.
10: Modified transmission.
15: Modified clutch.
20: Modified braking systems.
25: Modified accelerator systems.
30: Combined braking and accelerator systems (for licences issued before 28 November 2016).
31: Pedal adaptations and pedal safeguards.
32: Combined service brake and accelerator systems.
33: Combined service brake, accelerator, and steering systems.
35: Modified control layouts.
40: Modified steering.
42: Modified rear-view mirror(s).
43: Modified driving seats.
44: Modifications to motorbikes.
44 (1): Single operated brake.
44 (2): Adapted front wheel brake.
44 (3): Adapted rear wheel brake.
44 (4): Adapted accelerator.
44 (5): (Adjusted) manual transmission and manual clutch.
44 (6): (Adjusted) rear-view mirror(s).
44 (7): (Adjusted) commands (direction indicators, braking light, etc.).
44 (8): Seat height allowing the driver to balance the motorcycle during stopping and standing.
44 (11): Adapted foot rest.
44 (12): Adapted hand grip.
45: Motorbikes only with sidecar.
46: Tricycles only (for licences issued before 29 June 2014).
70: Exchange of licence.
71: Duplicate of licence.
78: Restricted to vehicles with automatic transmission.
79: Restricted to vehicles in conformity with the specifications stated in brackets on your licence.
79 (2): Restricted to category AM vehicles of the 3-wheel or light quadricycle type.
79 (3): Restricted to tricycles.
96: Allowed to drive a vehicle and trailer where the trailer weighs at least 750kg, and the combined weight of the vehicle and trailer is between 3,500kg and 4,250kg.
97: Not allowed to drive category C1 vehicles which are required to have a tachograph fitted.
101: Not for hire or reward (not to make a profit).
102: Drawbar trailers only.
103: Subject to certificate of competence.
105: Vehicle not more than 5.5 metres long.
106: Restricted to vehicles with automatic transmissions.
107: Not more than 8,250 kilograms.
108: Subject to minimum age requirements.
110: Limited to transporting persons with restricted mobility.
111: Limited to 16 passenger seats.
113: Limited to 16 passenger seats except for automatics.
114: With any special controls required for safe driving.
115: Organ donor.
118: Start date is for earliest entitlement.
119: Weight limit for vehicle does not apply.
121: Restricted to conditions specified in the Secretary of State’s notice.
122: Valid on successful completion of the Basic Moped Training Course. This does not apply to trial e-scooters.
125: Tricycles only (for licences issued before 29 June 2014).
Understanding these codes is crucial for compliance and ensuring you operate within the legal framework of your driving licence.
Driving HGVs and LGVs
Driving Licence Requirements:
To drive HGVs (Category C) or LGVs (Category C1), you must hold the appropriate driving licence with the necessary entitlements.
For Category C, you can drive vehicles over 3,500 kg with a trailer up to 750 kg.
For Category C1, you can drive vehicles weighing between 3,500 kg and 7,500 kg with a trailer up to 750 kg.
Age Requirements:
The minimum age to obtain a Category C licence is 18 years.
For a Category C1 licence, the minimum age is also 18 years.
Medical Standards:
Drivers of HGVs and LGVs must meet specific medical standards, which may include vision and hearing tests, as well as assessments of other medical conditions. Drivers must provide a medical declaration to ensure they meet these standards.
Driver Certificate of Professional Competence (CPC):
Drivers of HGVs and LGVs must complete a Driver CPC qualification, which includes initial training and ongoing periodic training (35 hours every five years) to ensure they are up to date with safety and driving regulations.
Tachograph Requirements:
Drivers must comply with tachograph regulations, which record driving hours, rest periods, and vehicle speeds. Compliance is essential for safety and legal accountability.
Additional Codes and Restrictions:
Similar to minibuses, certain codes may apply to HGVs and LGVs, such as:
NFHR (Not For Hire or Reward): Indicates that the driver is not allowed to accept payment for transporting goods commercially.
Other specific restrictions related to medical conditions or vehicle modifications may also apply.
Training and Certification:
Drivers may be required to complete additional training or certification for specialized vehicles, such as those carrying hazardous materials (ADR training) or operating vehicles with specific equipment (like cranes).
Driving Abroad:
Drivers must ensure they comply with the regulations of any country they are driving in. This includes understanding local laws regarding vehicle weights, emissions, and any additional driver certification requirements.
Driving a Minibus
To drive a minibus that has between nine and 16 passenger seats, you will typically need to hold Passenger-Carrying Vehicle (PCV) entitlement D1.
Guidance on Driving Minibuses
On 12 April 2018, new guidance was released concerning the driver licensing requirements for minibuses. Here are some key points:
Driver Licensing Requirements: This guidance outlines the rules for individuals who drive minibuses capable of carrying up to 16 passengers, exemptions for those volunteering without payment, and those driving for personal purposes (e.g., transporting family).
Licences Issued Before 1 January 1997: If you passed your car driving test before this date, you may have entitlement to drive minibuses on a voluntary basis, provided your licence hasn’t been medically restricted. This entitlement is indicated by category D1 with restriction code 79 (NFHR) on your licence, valid throughout the UK. Here, 'NFHR' stands for 'Not For Hire or Reward,' which means you cannot accept any payment, either cash or in kind, from passengers in exchange for transportation. This restriction is important to ensure that those using the vehicle do so for non-commercial purposes, promoting community service and volunteerism.
Medically Restricted Licences: If your licence is medically restricted or if you are over 70, you must meet higher medical standards to have your minibus entitlement reissued. If not renewed, you may still be able to drive minibuses under specific conditions.
Licences Without Minibus Entitlement: If your licence does not permit you to drive minibuses, you may still do so on behalf of a non-commercial organisation under certain conditions: you must have a full car licence, held it for at least two years, be over 21, receive no payment other than out-of-pocket expenses, and be driving for social purposes. The minibus must not weigh more than 3,500 kg (or 4,250 kg with specialist equipment) and you are not permitted to tow a trailer.
